Key Takeaways
- Ukrainian forces are skillfully exploiting Russia’s deployment of forces away from the Izyum-Kharkiv area to retake territory and threaten Russian GLOCs in the area, prompting demoralized responses from Russian milbloggers.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin attempted to deny the International Atomic Energy Agency’s (IAEA) September 6 report on the situation at the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP).
- Ukrainian forces continued strikes on Russian logistics nodes, manpower and equipment concentrations, transportation networks, and command and control points in Kherson Oblast.
- Russian and Ukrainian sources reported kinetic activity in northern Kherson Oblast and in western Kherson Oblast along the Kherson-Mykolaiv border.
- Russian forces conducted ground attacks north of Kharkiv City, northwest of Slovyansk, northeast of Siversk, south and northeast of Bakhmut, and northwest of Donetsk City.
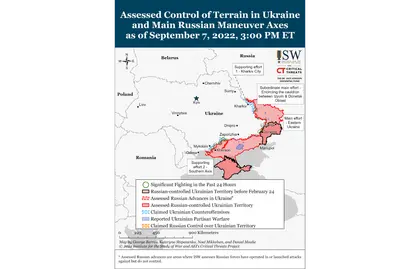
- Ukrainian forces gained 400 square kilometers of territory northwest of Izyum on September 6-7 as part of an opportunistic and highly effective counteroffensive in southeastern Kharkiv Oblast.
- Russian occupation authorities announced November 4 as the potential date for annexation referenda in occupied areas of Ukraine.
Ukrainian forces in southeastern Kharkiv Oblast are likely exploiting Russian force reallocation to the Southern Axis to conduct an opportunistic yet highly effective counteroffensive northwest of Izyum. Ukrainian forces likely used tactical surprise to advance at least 20km into Russian-held territory in eastern Kharkiv Oblast on September 7, recapturing approximately 400 square kilometers of ground. Russian sources claimed that Russian troops began deploying reinforcements to the area to defend against Ukrainian advances, and the Russian grouping in this area was likely understrength due to previous Russian deployments to support ongoing efforts to capture the remainder of Donetsk Oblast and support the southern axis.[1] Ukraine’s ongoing operations in Kherson Oblast have forced Russian forces to shift their focus to the south, enabling Ukrainian forces to launch localized but highly effective counterattacks in the Izyum area.[2] Russian milbloggers voiced concern that this Ukrainian counterattack seeks to cut ground lines of communication (GLOCs) to Russian rear areas in Kupyansk and Izyum, which would allow Ukrainian troops to isolate the Russian groupings in these areas and retake large swaths of territory.[3] These milbloggers used largely panicked and despondent tones, acknowledged significant Ukrainian gains, and claimed that the Ukrainian counteroffensive in the south may be a distraction from the ongoing actions in Kharkiv Oblast, which they name as the main Ukrainian effort.[4] The level of shock and frank discussion of Ukrainian successes by Russian milbloggers speaks to the scale of surprise achieved by Ukrainian forces, which is likely successfully demoralizing Russian forces. While it is unlikely that the southern counteroffensive and effort to attrit Russian forces in southern Ukraine is a feint for renewed operations in Kharkiv Oblast, Ukrainian forces likely took prudent advantage of a reallocation of Russian troops, equipment, and overall operational focus to launch localized counteroffensives toward critical points in Kharkiv Oblast.

EU Transfers €1.5 Bln Raised From Russian Assets for Ukraine
JOIN US ON TELEGRAM
Follow our coverage of the war on the @Kyivpost_official.
Russian President Vladimir Putin attempted to deny the International Atomic Energy Agency’s (IAEA) September 6 report on the situation at the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP). Putin claimed that there is no Russian military equipment on the grounds of the ZNPP other than Rosgvardia elements.[5] Rosgvardia elements have carried out both occupation functions and frontline combat operations during the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Putin’s admission that there are Rosgvardia elements on the plant’s grounds further confirms that Russian forces have militarized their presence at the ZNPP despite constant Russian denials. Putin also accused the IAEA of acting under Western pressure to not directly blame Ukraine of shelling the plant. As ISW previously assessed, the IAEA report was a coded yet damning condemnation of Russian activities at the ZNPP.[6]
Authors: Karolina Hird, Grace Mappes, George Barros, Layne Philipson, and Mason Clark
See the full report here.
You can also highlight the text and press Ctrl + Enter