Key Takeaways
- Russian President Vladimir Putin announced the illegal Russian annexation of four Ukrainian territories on September 30 without clearly defining the borders of those claimed territories.
- Putin announced that Russia’s usual autumn conscription cycle will start a month late on November 1, likely because Russia’s partial mobilization of Russian men is taxing the bureaucracy of the Russian military commissariats that would usually oversee the semi-annual conscription cycle.
- Russian officials could re-mobilize last year’s conscripts when their terms expire on October 1.
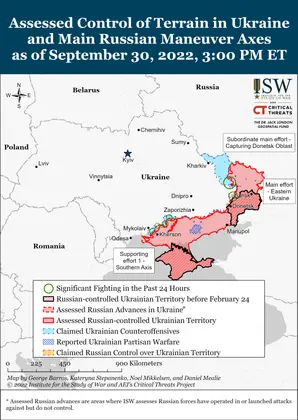
- Ukrainian forces will likely capture or encircle Lyman within the next 72 hours.
- Ukrainian military officials maintained operational silence regarding Ukrainian ground maneuvers in Kherson Oblast but stated that Ukrainian forces continued to force Russian troops into defending their positions.
- Russian troops continued ground assaults in Donetsk Oblast.
- Russian authorities continued efforts to coerce Russian participation in mobilization efforts, but will likely struggle to coerce participation as Russians continue to flee Russia for border states who welcome them.
- Russian officials are accepting bribes and engaging in other preferential treatment to prevent or ease the economic burden of mobilization on the wealthy.
- Russian authorities are continuing to deploy mobilized personnel to Ukraine without adequate training or equipment, and personnel are unlikely to be able to afford to provide their own supplies.
- Russian forces conducted a missile strike on a Ukrainian humanitarian convoy and attempted to blame the Ukrainian government.
Russian President Vladimir Putin announced the illegal Russian annexation of four Ukrainian territories on September 30 without clearly defining the borders of those claimed territories. Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov declined to specify the borders of the newly annexed territories in a September 30 conversation with reporters: “[the] Donetsk and Luhansk People’s Republics [DNR and LNR] were recognized by Russia within the borders of 2014. As for the territories of Kherson and Zaporizhia oblasts, I need to clarify this. We will clarify everything today.”[1] DNR head Denis Pushilin added that even the federal district into which the annexed territories will be incorporated remains unclear: “What will it be called, what are the borders—let’s wait for the final decisions, consultations are now being held on how to do it right.”[2] Russian officials may clarify those boundaries and administrative allocations in the coming days but face an inherent problem: Ukrainian forces still control large swathes of Donetsk and Zaporizhia and some areas of Luhansk and Kherson oblasts, a military reality that is unlikely to change in the coming months.
JOIN US ON TELEGRAM
Follow our coverage of the war on the @Kyivpost_official.
Putin likely rushed the annexation of these territories before making even basic administrative decisions on boundaries and governance. Russian officials have therefore not set clear policies or conditions for proper administration. Organizing governance for these four forcibly annexed oblasts would be bureaucratically challenging for any state after Russian forces systematically killed, arrested, or drove out the Ukrainian officials who previously ran the regional administrations. But the bureaucratic incompetence demonstrated by the Kremlin’s attempted partial mobilization of Russian men suggests that Russian bureaucrats will similarly struggle to establish governance structures over a resistant and unwilling population in the warzone that is Russian-occupied Ukrainian territory.

EU Transfers €1.5 Bln Raised From Russian Assets for Ukraine
Putin announced that Russia’s usual autumn conscription cycle will start a month late on November 1, likely because Russia’s partial mobilization of Russian men is taxing the bureaucracy of the Russian military commissariats that would usually oversee the semi-annual conscription cycle.[3] Putin’s September 30 decree calls for 120,000 Russian conscripts—7,000 fewer than in autumn 2021. Neither Putin’s decree nor subsequent official statements clarified whether Ukrainian civilians of conscription age (18-27) in Russia’s newly-annexed occupied Ukrainian territories will be liable for conscription. A representative of Russia’s Main Organizational and Mobilization Directorate, Rear Admiral Vladimir Tsimlyansky, claimed that no autumn 2022 conscripts would fight in the “special operation” in Ukraine, a promise Putin also made (and broke) about the autumn 2021 and spring 2022 conscripts.[4] Russian conscripts are not legally deployable overseas until they have received at least four months of training unless Putin were to declare martial law.[5] Russia’s illegal annexation of occupied areas in Ukraine likely removes this problem within the framework of Russian Federation law, which may be part of the reason for Putin’s rush in announcing the annexation.
Russian officials could re-mobilize last year’s conscripts when their terms expire on October 1. Tsimlyansky emphasized on September 30 that all Russian conscripts whose terms have expired—meaning those conscripted in autumn 2021—will be released from service and returned to their residences “in a timely manner.”[6] Once released, autumn 2021 conscripts will technically become part of the Russian reserves, making them legally mobilizable under Putin’s September 21 partial mobilization order.
Putin invited some Russian milbloggers and war correspondents who have previously criticized the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) for a lack of transparency about Russian progress in Ukraine to attend his annexation speech in Moscow.[7] Russian state media has been increasingly featuring some milbloggers on federal television channels as well, which likely indicates that Putin is attempting to secure the support of these nationalist and pro-war figures rather than censor them. The milblogger presence in Moscow may also explain why several prominent Telegram channels had limited or no coverage of daily frontline news on September 29.
See the full report here.
You can also highlight the text and press Ctrl + Enter